Nanostructured Large-area Antibacterial Surfaces (nLABS)
Kofi J. Brobbey
Laboratory of Paper Coating and Converting
E-mail: Kofi.brobbey@abo.fi
Co-operation partners: Tampere University of Technology/Aerosol Physics, Turku University/ Medical Microbiology
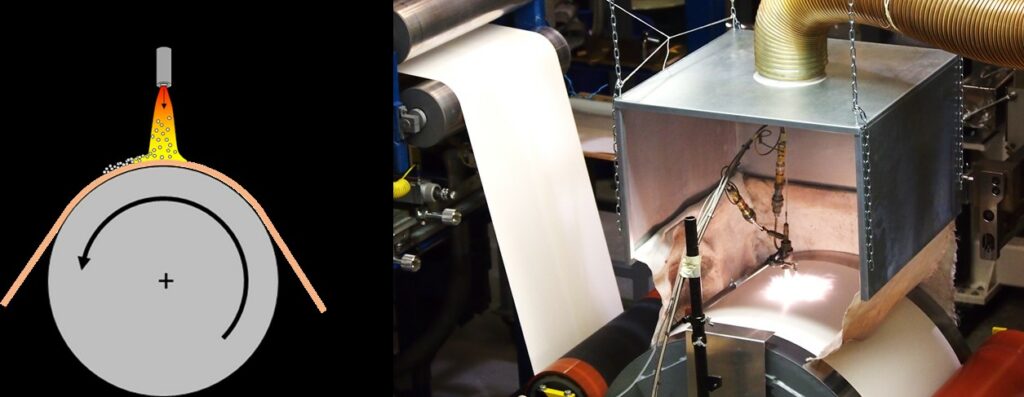
Drug-resistant bacteria have been a problem in recent years, especially in hospital environments, resulting in a growing number of fatalities annually. As a result, alternative measures that can control these drug-resistant bacteria are need. The use of an antibacterial surface could be used to eliminate/reduce contact transfer of pathogenic bacteria. Nanoparticles that possess antibacterial properties, such as silver, have shown promise in controlling drug-resistant bacteria. However, the ability to synthesize such nanoparticles in a roll-to-roll process onto a large-area substrate has been a challenge. In this research, large-area antibacterial surfaces are produced using a roll-to-roll process. An aerosol deposition technique called Liquid Flame Spray (LFS) is used to deposit metal and metal-oxide nanoparticles onto different substrates to produce antibacterial surfaces. The LFS deposition process does not produce effluents, and nanoparticles can be produced at speeds exceeding 300m/min in a roll-to-roll process. Therefore, using the LFS technology to produce antibacterial surfaces would be beneficial in the overall fight against drug-resistant bacteria. Practical applications include roll-to-roll production of antibacterial paper and textiles.
Publications
- One-step flame synthesis of silver nanoparticles for roll-to-roll production of antibacterial paper, Applied Surface Science https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.05.143
- Controlled time release and leaching of silver nanoparticles using a thin immobilizing layer of aluminum oxide – Thin Solid Films https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2017.09.060
- Antimicrobial characterization of silver nanoparticle-coated surfaces by ‘Touch Test’ method. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications. 10.2147/NSA.S1395+05
- Efficacy of Natural Plant Extracts in Antimicrobial Packaging Systems – Journal of Applied Packaging Research http://scholarworks.rit.edu/japr/vol9/iss1/6/

